The purpose of the QSIR Programme is to provide a platform for NHS organisations and systems to build improvement capability at scale in line with the aims set out in the Long Term Plan.
The QSIR programmes are delivered in a variety of formats to suit different levels of improvement experience and are supported by publications that guide participants in the use of tried and tested improvement tools, and featured approaches, as well as encouraging reflective learning.
The QSIR programme was recognised in the NHS Delivery and Continuous Improvement Review as an important resource for building improvement capability across the health and social care system. With Aqua’s expertise also recognised in the review, you can be confident that we can effectively support your organisation to embed a culture and system for continuous improvement.
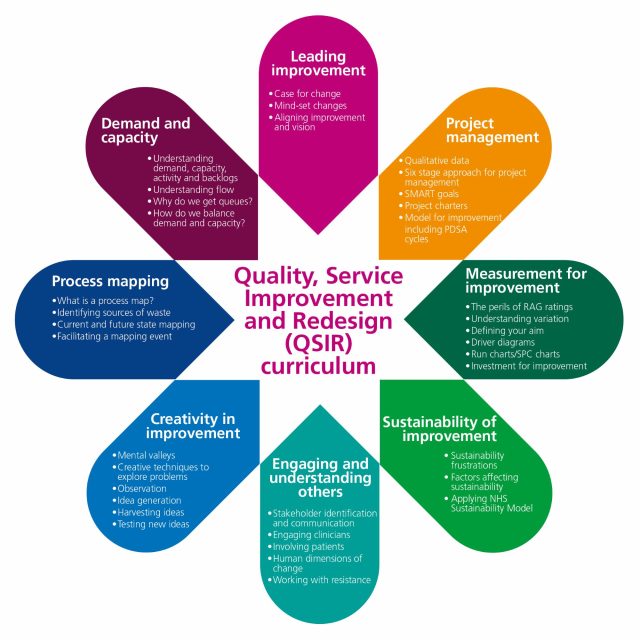
View the full list of QSIR tools:
QSIR Fundamentals
This 1-day programme offers participants an introduction to a range of tried and tested service improvement tools and approaches, giving them the confidence and skills to start on their improvement journey.
QSIR Virtual
The QSIR Virtual programme was codesigned with QSIR associates to support QSIR faculties in continuing to build improvement capability during the COVID-19 reset and recovery period. The programme has been designed to cover all concepts from the QSIR Fundamentals programme and more, typically through 8 1-hour modules supplemented by QSIR Cafés and Virtual Action Learning Sets. The QSIR Virtual programme offers a more advanced alternative to the QSIR Fundamentals programme and starts participants towards the QSIR Practitioner course.
QSIR Practitioner
QSIR Practitioner is an 8-module programme that is typically delivered face-to-face over 5 days and is aimed at providing participants with the know-how to design and implement more efficient and productive services. It aims to enable participants to initiate, progress and work towards completing a service or quality improvement project through the development of their skills and knowledge supported by a range of tools and products from the NHS.
QSIR College
Individuals wishing to register for QSIR College will have executive sponsorship to establish a local QSIR teaching faculty as part of the organisation’s approach to developing and embedding improvement capability, and will have successfully completed all 8 modules of the QSIR Practitioner programme. The college is a short virtual assessment testing participants on their skills, knowledge, and comprehension. Once successfully completed, candidates will be accredited as associate members of the QSIR teaching faculty and will have access to deliver QSIR in their local organisations and/or systems. They will also join the QSIR teaching faculty associate network, providing them with the opportunity to share learning across the health and care sector, and supporting the future development of QSIR programmes.

The QSIR College programme offers NHS organisations and health and care systems a unique opportunity to develop improvement capability within their organisation or across their system, enabling them to rapidly build up a sustainable local skills base as part of their wider approach to managing quality and/or developing a quality management system. QSIR College is designed to develop candidates to become associate members of the QSIR teaching faculty and go on to upskill other staff across their organisation or within their system.
Participants in QSIR College will learn how to train clinical and non-clinical colleagues in the QSIR programmes, providing them with the know-how to design and implement more efficient user and patient-centred services. Based on tried and tested tools and approaches, QSIR covers the breadth of service improvement skills.
The programme is designed for both clinical and non-clinical staff with experience in service improvement. Candidates need to be committed to working as a member of their local QSIR teaching faculty to roll out the QSIR programmes within their organisation or across their system.

Prospective QSIR College candidates will have successfully completed all 8 modules of the QSIR Practitioner programme. QSIR College involves a short virtual assessment testing participants on their skills, knowledge and comprehension. Only those who successfully meet all assessment criteria will be accredited as associate members of the QSIR teaching faculty, and therefore qualified to deliver QSIR within their organisation or system.
It is essential that each applicant organisation or system demonstrates they are prepared to support, enable and champion their candidates to fully benefit from the programme and also successfully roll out QSIR within their organisation/across their system.
If you’re interested in developing a QSIR teaching faculty or would like learn more about our range of offers, you can contact our faculty members at enquiries@aqua.nhs.uk.