Medicines optimisation
Did you know?
- One quarter of the population has a long-term condition
- One quarter of people over 60 have two or more long-term conditions
- With an ageing population, the use of multiple medicines (known as polypharmacy) is increasing
- Between 30-50% of medicines prescribed for long-term conditions are not taken as intended
Taken from: NICE: Medicines Optimisation Quality Standard
Medicines optimisation looks at the value which medicines deliver, making sure they are clinically-effective and cost-effective. It is about ensuring people get the right choice of medicines, at the right time, and are engaged in the process by their clinical team.
This graphic shows how this works:
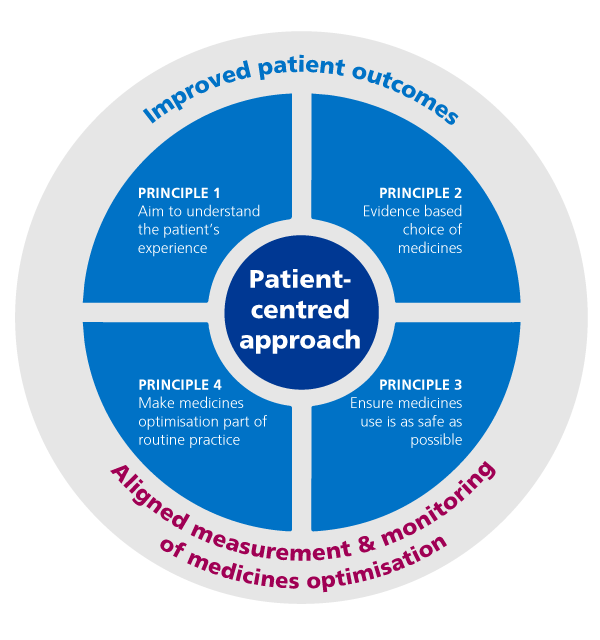
Medicines optimisation explained
The goal of medicines optimisation is to help patients to:
- improve their outcomes;
- take their medicines correctly;
- avoid taking unnecessary medicines;
- reduce wastage of medicines;
- and improve medicines safety.
NHS England supports the Royal Pharmaceutical Society guidance Medicines Optimisation: helping patients make the most of medicines, which has been developed in collaboration with patients, the medical and nursing professions and the pharmaceutical industry.
NICE has also published guidance: Medicines optimisation: the safe and effective use of medicines to enable the best possible outcomes.
Find out more
Get more information on medicines optimisation:
- Operational note: Commissioning recommendations following the national procurement for medical retinal vascular medicines – National procurement for Anti-VEGF and Intravitreal Corticosteroids
- Regional Medicines Optimisation Committees – The RMOCs have been set up to drive the changes that are needed in prescribing and medicines use, including reducing the waste.
- Improving health outcomes from medicines – This section is about improving patient outcomes through developing patient information, implementing clinically effective prescribing and medicines reviews, and making the best use of the clinical skills of pharmacy teams.
- Reducing the overuse of antibiotics – Work is underway to support prescribers in their role in tackling anti-microbial resistance.
- Biological and generic medicines – This is about increasing the use of best value biological and generic medicines, including biosimilar medicines where appropriate, to make millions of pounds worth of savings for reinvesting in NHS treatments.
- Decreasing or stopping the use of ineffective medicines – NHS England is working to ensure there is a clear and consistent approach to prescribing across England, and to decrease or stop the use of medicines which are not clinically-effective or cost-effective.
- Implementing the quality and innovation goals – known as a ‘CQUIN’ – for medicines optimisation within specialised services is a priority for secondary care.
- Medicines optimisation dashboard.
